|
All variables must be
declared
before
they can be used. |
How to declare a
variable:
1. Choose the type you
need.
2. Choose a name for
the variable.
3. Use the following
format for a declaration statement:
datatype variable identifier;
4. You may declare
more than one variable of the same
type by separating the
variable names with commas.
int
age, weight, height;
5. You may initialize
a variable (place a value into the
variable location) in a
declaration statement.
double mass = 3.45;
|
When you declare a variable,
Java reserves memory locations of sufficient size to store the variable type. The actual data values will be
stored in these memory locations.
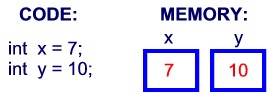
 |
Variables
that are not initialized are NOT empty. If you do not
initialize your variables, they will contain junk
("garbage") values left over from the program that last
used the memory they occupy, until such time as the
program places a value at that memory location. |
Constant Variables
Using
final you can define variables whose values
never change. You MUST place an initial value into
such a
"constant" variable. If you do not place this initial
value, Java will never let you assign a value at a later
time because you cannot do anything to change the value of
a final (constant) variable.
final int ageLimit = 21; // this value cannot be changed |
|
Java will
allow you to declare a variable anywhere in the program as
long as the variable is declared before you use it.
A good programming practice is to declare
variables near the top of the program. Declaring variables
in this manner makes for easier readability of the
program. |
 |
|