|
The formula used with Bernoulli
trials computes the binomial probability of obtaining
exactly "r" events in "n" trials:
|
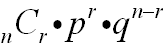
|
n = number of trials
r = number of specific events you wish to
obtain
p = probability that the event will occur
q = probability that the event will not
occur
(q = 1 - p, the
complement of the event) |
If you enter the formula directly on
the home screen, be careful
to use parentheses when entering the
exponent of n - r (or do the subtraction mentally
and enter your calculation).
|
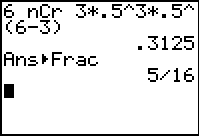
Consider a problem
where
n = 6, r = 3, and p = 50%
(so, p = .5 and q =
.5, where q = 1 - p)
(Remember, the function
nCr is
found under
MATH
→ PRB #3 nCr
and requires that the first value, n, be entered
before the function is called.) |
 |
The easiest way to utilize the calculator to solve this formula is
to engage the binompdf function:
|
binompdf( |
binomial distribution probability density
function, which is:
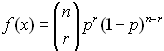 where where
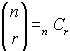
(When using this built-in function there is no need to
type in the formula - YEA!!) |
|
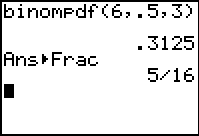
Consider, again, a problem where
n = 6, r = 3, and p = 50%
(Remember, the function
binompdf is found under
DISTR (2nd VARS), arrow down to #0 binompdf
and the parameters are:
binompdf (number of trials,
probability of occurrence, number of specific events) |
|
|

